3D Imaging - Services
Part Inspection Lab
We help companies thoroughly investigate
parts & assemblies with our high quality
3D Imaging services paired with
expert analytical support.


PHASE ONE
CONSULTATION
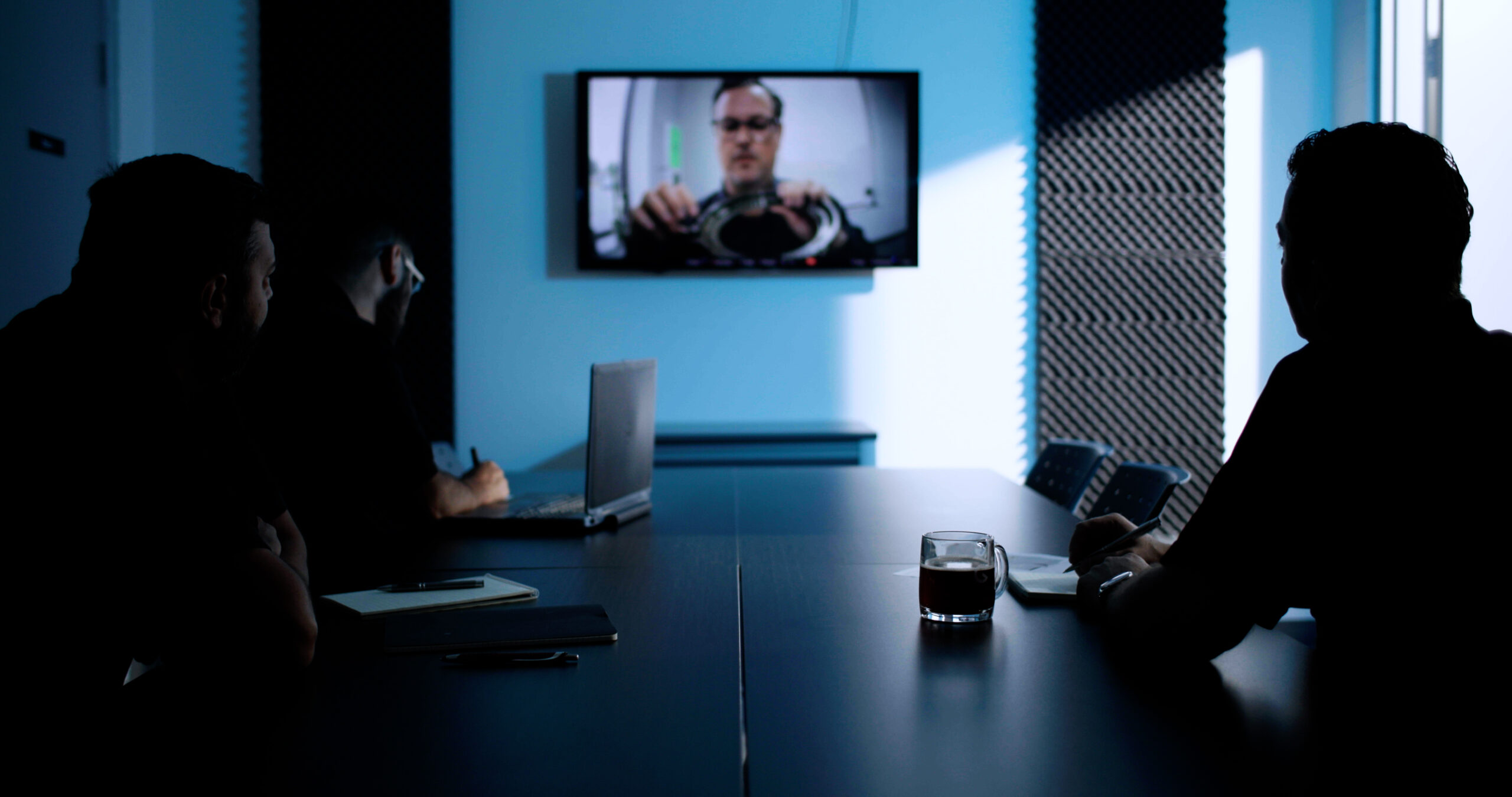
After the initial inquiry, our services begin by having an in-depth discussion with the inquiring individual and interested parties. If the fit is right for our 3D imaging services, the feasibility review considers part/assembly type, material, regions of interest, and the objective for the CT scan.
PHASE TWO
SYSTEM MATCHING
We then match the NDT or Metrology inspection need with one of our many and highly diverse CT imaging machines. Our industrial lab utilizes 100kv, 150kv, 225kv, 450kv, and 3MEV linear accelerator CT scanning systems with LDA’s and flat panel detectors



PHASE THREE
ANALYSIS
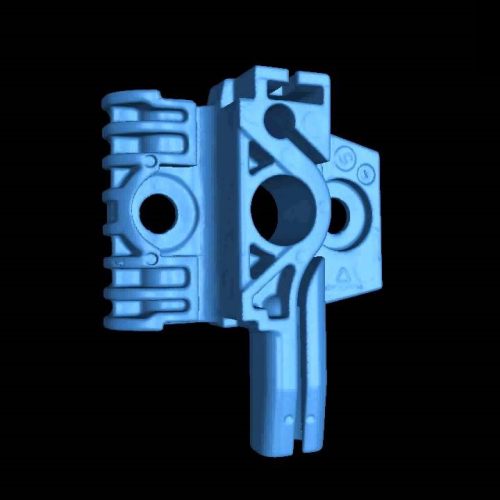
Depending on the project, we analyze the reconstructed (3D imaging) results for either material or geometry based output requirements.
Material reporting is based upon internal density variations or percent volume changes. These types of 3D imaging analysis include :
Visualizing virtual cross-sectional slices
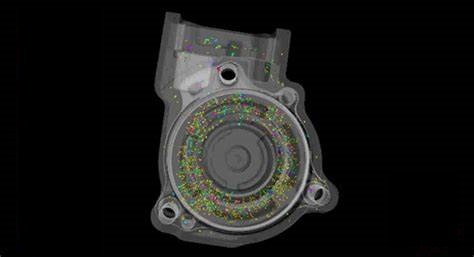
Porosity / Inclusion Analysis (Color coded voids, inclusions, and micro pores by volumetric size or percentage)
Enhanced Porosity (Automotive Industry Specific, P201 – 50097, P202 – 50098, P203 Analysis)
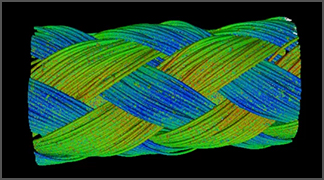
Fiber Analysis (Color coded fiber directional reporting)


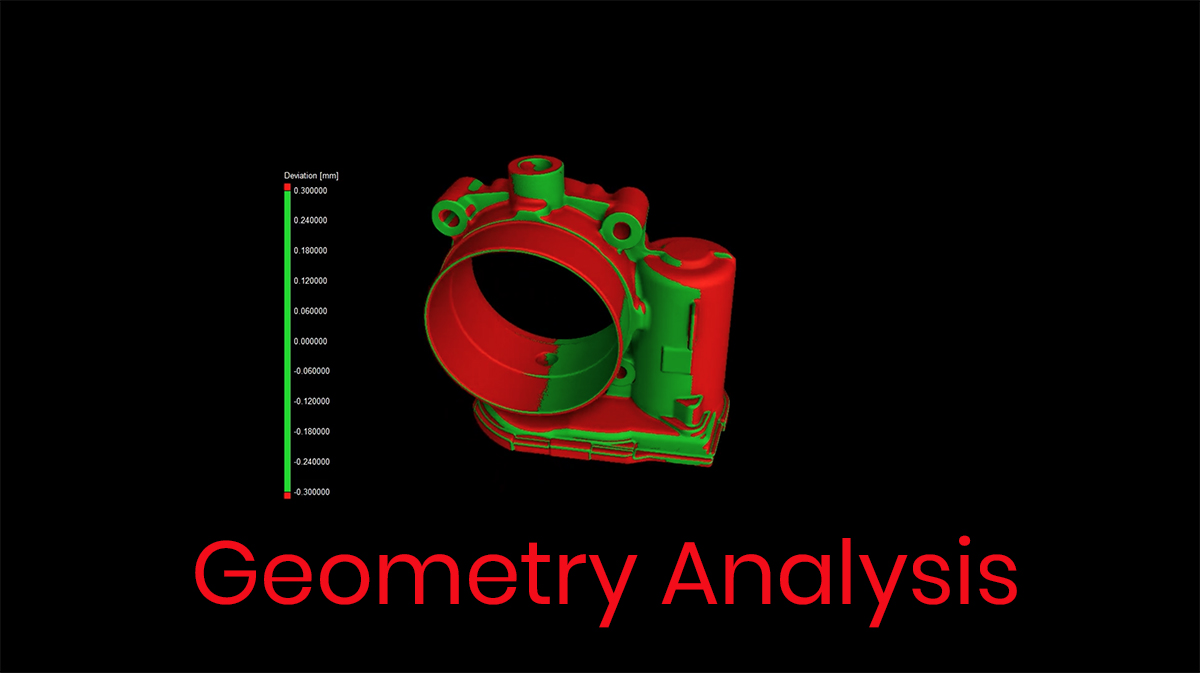
Geometry reporting is based upon measurement variations or dimensioning requirements. These types of 3D imaging analysis include :
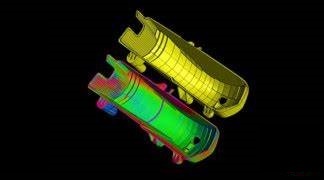
Part to CAD / Part Comparison (Color coded variations from nominal or another identical part. Alignment by: RPS, 3-2-1 alignment, best fit, sequential)
Wall Thickness Analysis (Color-coded results identifying insufficient or excessive wall thicknes)
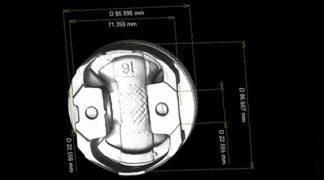
First Article Inspection (Tolerancing based upon part print dimensions)
Enhanced FAI (AS9102 Form 3 Reporting)
Reverse Engineering (Generation of a STL file with internal & external part geometry)



PHASE FOUR
REVIEW
As all projects are unique, each project is finalized between our lab and the customers key decision makers over a results web conference. If required, output deliverables can vary between picture files, excel files, presentations, 3D imaging / CT dataset viewing software, or in some cases STL files.

Need more info on 3D imaging?
Review our knowledge section below.
Overview
3D imaging can be traced back to the early 1500’s in Leonardo Da Vinci’s work. In regards to industrial applications, technological advancements and specialized inspection techniques have allowed users to obtain accurate and timeless 3D data on objects, by providing a 3D image for testing purposes.
What is 3D Imaging?
The technology is a technique to develop or create the illusion of depth in an image. The technology has become a very useful factor for industrial applications to assist in quality control processes. 3D imaging is the process of manipulating 2D data into three dimensional format, creating the illusion of depth. Many different technologies are able to assist with this process, in order to develop a 3D rendering for inspection and testing purposes.
Common Types of Industrial 3D Imaging
3D Structured Light – Structured light is the process of using a focused white or colored light which is then picked up by a specialized camera and read into a program to capture external features of an object which is then turned into a polygon based surface.
3D laser imaging – also known as 3D laser scanning, 3D laser imaging is the process of capturing data using laser beams which are exposed to the surface of an object. The captured data develops a 3D rendering with the assistance of a software.
CT imaging – Computed Tomography (CT) imaging is a radiographic testing technique, utilizing an x-ray source to penetrate through materials and capturing 2D x-ray tomography slices at pre-determined increments for an object that is rotating 360 degrees. As the object rotates and 2D x-ray images are captured, a specialized software is used to reconstruct the 2D images and develop a 3D rendering of the object, which is available for further internal and external part analysis.
3D x-ray imaging – 3D x-ray is the process of capturing 2D x-ray images from different angles of an object, which can be used to reconstruct and create the illusion of depth. For the purpose of 3D x-ray, these 2D x-ray images are viewed and analyzed independently to focus on certain areas of an object.
Applications
There are multiple uses for industrial applications, regardless of industry and type of part being inspected. The purpose of a 3D image is to provide users with a realistic replica of the object for quality control purposes. Some of the most common applications for span across the aerospace, automotive and medical device industry include:
- Reverse Engineering
- Part to CAD comparison – test for consistency
- Internal part analysis
- Analyze fit & function of part
- Failure analysis
- Identify internal defects such as cracks or voids
- Dimensional analysis
- Wall thickness analysis
- Part to part comparison
Benefits
3D imaging allows users to replicate and analyze parts and objects in full 3D form. This opens up limitless opportunities for quality control measures and allows for an exceptional outlet for visualizing the object in digital form. The most common benefits include:
- Nondestructive techniques
- Fast and accurate part results
- Availability for extensive analysis
- Ensure part consistency and reliability
- Allows perspective on quality control

